Catalyst design in C–H activation: a case study in the use of binding free energies to rationalise intramolecular directing group selectivity in iridium catalysis†
Abstract
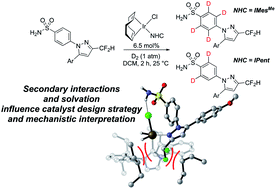
Remote directing groups in a bifunctional molecule do not always behave independently of one another in C–H activation chemistries. A combined DFT and experimental mechanistic study to provide enhanced Ir catalysts for chemoselective C–H deuteration of bifunctional aryl primary sulfonamides is described. This provides a pharmaceutically-relevant and limiting case study in using binding energies to predict intramolecular directing group chemoselectivity. Rational catalyst design, guided solely by qualitative substrate–catalyst binding free energy predictions, enabled intramolecular discrimination between competing ortho-directing groups in C–H activation and delivered improved catalysts for sulfonamide-selective C–H deuteration. As a result, chemoselective binding of the primary sulfonamide moiety was achieved in the face of an intrinsically more powerful pyrazole directing group present in the same molecule. Detailed DFT calculations and mechanistic experiments revealed a breakdown in the applied binding free energy model, illustrating the important interconnectivity of ligand design, substrate geometry, directing group cooperativity, and solvation in supporting DFT calculations. This work has important implications around attempts to predict intramolecular C–H activation directing group chemoselectivity using simplified monofunctional fragment molecules. More generally, these studies provide insights for catalyst design methods in late-stage C–H functionalisation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...