The Ras dimer structure†
Abstract
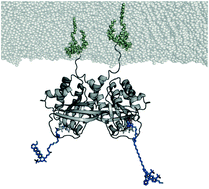
Oncogenic mutated Ras is a key player in cancer, but despite intense and expensive approaches its catalytic center seems undruggable. The Ras dimer interface is a possible alternative drug target. Dimerization at the membrane affects cell growth signal transduction. In vivo studies indicate that preventing dimerization of oncogenic mutated Ras inhibits uncontrolled cell growth. Conventional computational drug-screening approaches require a precise atomic dimer model as input to successfully access drug candidates. However, the proposed dimer structural models are controversial. Here, we provide a clear-cut experimentally validated N-Ras dimer structural model. We incorporated unnatural amino acids into Ras to enable the binding of labels at multiple positions via click chemistry. This labeling allowed the determination of multiple distances of the membrane-bound Ras-dimer measured by fluorescence and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. In combination with protein–protein docking and biomolecular simulations, we identified key residues for dimerization. Site-directed mutations of these residues prevent dimer formation in our experiments, proving our dimer model to be correct. The presented dimer structure enables computational drug-screening studies exploiting the Ras dimer interface as an alternative drug target.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...