Coacervate formation studied by explicit solvent coarse-grain molecular dynamics with the Martini model†
Abstract
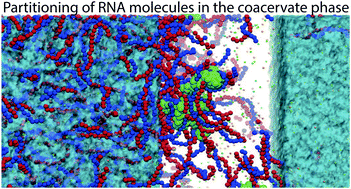
Complex coacervates are liquid–liquid phase separated systems, typically containing oppositely charged polyelectrolytes. They are widely studied for their functional properties as well as their potential involvement in cellular compartmentalization as biomolecular condensates. Diffusion and partitioning of solutes into a coacervate phase are important to address because their highly dynamic nature is one of their most important functional characteristics in real-world systems, but are difficult to study experimentally or even theoretically without an explicit representation of every molecule in the system. Here, we present an explicit-solvent, molecular dynamics coarse-grain model of complex coacervates, based on the Martini 3.0 force field. We demonstrate the accuracy of the model by reproducing the salt dependent coacervation of poly-lysine and poly-glutamate systems, and show the potential of the model by simulating the partitioning of ions and small nucleotides between the condensate and surrounding solvent phase. Our model paves the way for simulating coacervates and biomolecular condensates in a wide range of conditions, with near-atomic resolution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...