Encapsulation of tricopper cluster in a synthetic cryptand enables facile redox processes from CuICuICuI to CuIICuIICuII states†
Abstract
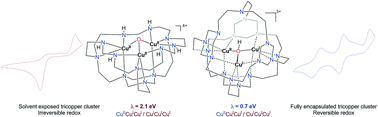
One-pot reaction of tris(2-aminoethyl)amine (TREN), [CuI(MeCN)4]PF6, and paraformaldehyde affords a mixed-valent [TREN4CuIICuICuI(μ3-OH)](PF6)3 complex. The macrocyclic azacryptand TREN4 contains four TREN motifs, three of which provide a bowl-shape binding pocket for the [Cu3(μ3-OH)]3+ core. The fourth TREN caps on top of the tricopper cluster to form a cryptand, imposing conformational constraints and preventing solvent interaction. Contrasting the limited redox capability of synthetic tricopper complexes reported so far, [TREN4CuIICuICuI(μ3-OH)](PF6)3 exhibits several reversible single-electron redox events. The distinct electrochemical behaviors of [TREN4CuIICuICuI(μ3-OH)](PF6)3 and its solvent-exposed analog [TREN3CuIICuIICuII(μ3-O)](PF6)4 suggest that isolation of tricopper core in a cryptand enables facile electron transfer, allowing potential application of synthetic tricopper complexes as redox catalysts. Indeed, the fully reduced [TREN4CuICuICuI(μ3-OH)](PF6)2 can reduce O2 under acidic conditions. The geometric constraints provided by the cryptand are reminiscent of Nature's multicopper oxidases (MCOs). For the first time, a synthetic tricopper cluster was isolated and fully characterized at CuICuICuI (4a), CuIICuICuI (4b), and CuIICuIICuI (4c) states, providing structural and spectroscopic models for many intermediates in MCOs. Fast electron transfer rates (105 to 106 M−1 s−1) were observed for both CuICuICuI/CuIICuICuI and CuIICuICuI/CuIICuIICuI redox couples, approaching the rapid electron transfer rates of copper sites in MCO.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...