Template-assisted design of monomeric polyQ models to unravel the unique role of glutamine side chains in disease-related aggregation†
Abstract
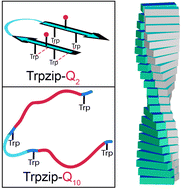
Expanded polyglutamine (polyQ) sequences cause numerous neurodegenerative diseases which are accompanied by the formation of polyQ fibrils. The unique role of glutamines in the aggregation onset is undoubtedly accepted and a lot structural data of the fibrils have been acquired, however side-chain specific structural dynamics inducing oligomerization are not well understood yet. To analyze spectroscopically the nucleation process, we designed various template-assisted glutamine-rich β-hairpin monomers mimicking the structural motif of a polyQ fibril. In a top-down strategy, we use a template which forms a well-defined stable hairpin in solution, insert polyQ-rich sequences into each strand and monitor the effects of individual glutamines by NMR, CD and IR spectroscopic approaches. The design was further advanced by alternating glutamines with other amino acids (T, W, E, K), thereby enhancing the solubility and increasing the number of cross-strand interacting glutamine side chains. Our spectroscopic studies reveal a decreasing hairpin stability with increased glutamine content and demonstrate the enormous impact of only a few glutamines – far below the disease threshold – to destabilize structure. Furthermore, we could access sub-ms conformational dynamics of monomeric polyQ-rich peptides by laser-excited temperature-jump IR spectroscopy. Both, the increased number of interacting glutamines and higher concentrations are key parameters to induce oligomerization. Concentration-dependent time-resolved IR measurements indicate an additional slower kinetic phase upon oligomer formation. The here presented peptide models enable spectroscopic molecular analyses to distinguish between monomer and oligomer dynamics in the early steps of polyQ fibril formation and in a side-chain specific manner.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...