Selective hydrogenation of oleic acid to fatty alcohols over a Rh–Sn–B/Al2O3 catalyst: kinetics and optimal reaction conditions†
Abstract
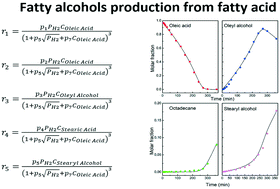
The selective hydrogenation of oleic acid to oleyl alcohol over a Rh(1 wt%)–Sn(4 wt%)–B/Al2O3 catalyst was studied. A comprehensive set of experimental data was used for elucidating the reaction mechanism. In the range of reaction conditions of this work, the optimal conditions found were 290 °C and 2 MPa, with a yield of 82–83% of oleyl alcohol. Kinetic models were written which considered the whole network of reactions taking place: double bond hydrogenation, acid hydrogenation to alcohol, and esterification of acids and alcohols. Different combinations of elementary steps led to the formulation of a big number of models. Models posing the surface reactions as rate-limiting fitted the data better. Adsorption of the acids, the alcohols or hydrogen was not rate-limiting. The best-fit model had the following hypotheses: (i) only one kind of adsorption site is needed for all species and reactions; (ii) H2 is dissociatively adsorbed; (iii) fatty molecules are adsorbed on only one site; (iv) pairwise insertion of H to fatty molecules is the rate-limiting step; (v) reduction of the carboxylate group occurs via an aldehyde intermediate that is subsequently hydrogenated to the corresponding alcohol; (vii) hydrogen and oleic acid are the main adsorbates; (vii) heavy esters are formed but do not contribute as intermediates of the main mechanism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...