Reductive C(sp3)–C(sp3) homo-coupling of benzyl or allyl halides with H2 using a water-soluble electron storage catalyst†
Abstract
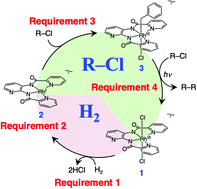
This paper reports the first example of a reductive C(sp3)–C(sp3) homo-coupling of benzyl/allyl halides in aqueous solution by using H2 as an electron source {turnover numbers (TONs) = 0.5–2.3 for 12 h}. This homo-coupling reaction, promoted by visible light, is catalysed by a water-soluble electron storage catalyst (ESC). The reaction mechanism, and four requirements to make it possible, are also described.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...