Unexpected reactivity related to support effects during xylose hydrogenation over ruthenium catalysts†
Abstract
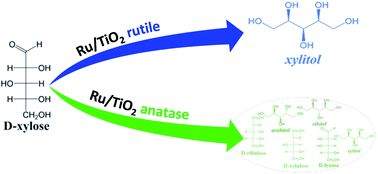
Xylose is a major component of hemicelluloses. In this paper, its hydrogenation to xylitol in aqueous medium was investigated with two Ru/TiO2 catalysts prepared with two commercial TiO2 supports. A strong impact of the support on catalytic performance was evidenced. Ru/TiO2-R led to fast and selective conversion of xylose (100% conversion in 2 h at 120 °C with 99% selectivity) whereas Ru/TiO2-A gave a slower and much less selective transformation (58% conversion in 4 h at 120 °C with 17% selectivity) with the formation of several by-products. Detailed characterization of the catalysts with ICP, XRD, FTIR, TEM, H2 chemisorption, N2 porosimetry, TPR and acid–base titration was performed to elucidate the role of each support. TiO2-R has a small specific surface area with large ruthenium nanoparticles in weak interaction with the TiO2 support and no acidity, whereas TiO2-A is a mesoporous material with a large specific surface area that is mildly acidic, and bears small ruthenium particles in strong interaction with the TiO2 support. The former was very active and selective for xylose hydrogenation to xylitol whereas the latter was less active and poorly selective. Moreover, careful analysis of the reaction products also revealed that anatase TiO2 can catalyze undesired side-reactions such as xylose isomerisation to various pentoses, and therefore the corresponding unexpected polyols (arabitol, ribitol) were produced during xylose conversion by hydrogenation. In a first kinetic approach, a simplified kinetic model was built to compare quantitatively intrinsic reaction rates of both catalysts. The kinetic constant for hydrogenation was 20 times higher for Ru/TiO2-R at 120 °C.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...