Polytriphenylamine composites for energy storage electrodes: effect of pendant vs. backbone polymer architecture of the electroactive group†
Abstract
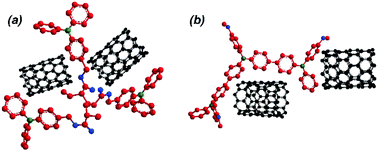
Polymers are an increasingly used class of materials in semiconductors, photovoltaics and energy storage. Polymers bearing triphenylamine (TPA) or its derivatives in their structures have shown promise for application in electrochemical energy storage devices. The aim of this work is to systematically synthesize polymers bearing TPA units either as pendant groups or directly along the backbone of the polymer and evaluate their performance as electrochemical energy storage electrode materials. The first was obtained via radical polymerization of an acrylate monomer bearing TPA as a side group, resulting in a non-conjugated polymer with individual redox active sites (rP). The latter was obtained by oxidative polymerization of a substituted TPA, resulting in a conjugated polymer with TPA units along its backbone (cP). These polymers were then developed into electrodes by separately blending them with multi-wall carbon nanotubes (rC and cC). The electrodes were characterized and their charge storage stability and mechanical properties were investigated for up to 1000 cycles by cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge–discharge measurements and nanoindentation. The results show that cC offers a higher initial charge capacity than rC as well as improved carbon nanotube dispersion due to its conjugated structure. Although the improved dispersion results in a higher elastic modulus for cC (compared to rC), the stiffer nature of cP made it more vulnerable to degrade upon repetitive volumetric change, while with rP, the decoupled acrylate monomer remained more protected when its redox active units of TPA underwent charge–discharge cycling.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...