The relationship between basic group resonance and quantum yield of high efficiency red light fluorescent solutions
Abstract
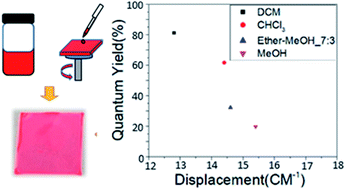
Compared with rare earth elements and heavy metal elements, rare-earth-element-free fluorescent films can greatly reduce environmental hazards. In this study, we use a solution method to produce the fluorescent films. The film thickness is 10 μm, which can maintain fluorescent light intensity in an environment with an average humidity of 55.1 (RH%) after encapsulation. We also find that the type of solvent affects the resonance position of the C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N functional group in DCJTB at a wavenumber of 2196 (cm−1), measured with Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The functional group is affected by the polar effect with its displacement decreasing with the quantum yield. Finally, we successfully made a fluorescent solution with a resonance displacement of only 12.8 (cm−1) for the C
N functional group in DCJTB at a wavenumber of 2196 (cm−1), measured with Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The functional group is affected by the polar effect with its displacement decreasing with the quantum yield. Finally, we successfully made a fluorescent solution with a resonance displacement of only 12.8 (cm−1) for the C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N functional group with the quantum yield being as high as 81.3% and a fluorescent film with a quantum yield as high as 84.8%.
N functional group with the quantum yield being as high as 81.3% and a fluorescent film with a quantum yield as high as 84.8%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...