A low-temperature hydrothermal synthesis of submicron spherical BaF2
Abstract
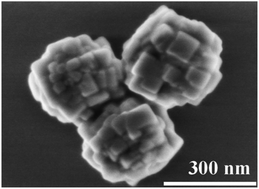
The sub-micron spherical barium fluoride (BaF2) was successfully synthesized via a low-temperature hydrothermal method using ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt (EDTA-2Na) as the chelating agent. The effect of pH, the molar ratio of EDTA to Ba2+, barium hydroxide octahydrate (Ba(OH)2·8H2O) concentration, hydrofluoric acid (HF) concentration, hydrothermal temperature and time, on the formation of spherical BaF2 were investigated. The formation mechanism of spherical BaF2 has been proposed based on the experimental results. The results show that the spherical BaF2, with an average size of 346.9 nm, is formed by the self-assembly of nanocubes. The optimized synthesis conditions are: pH = 14, EDTA-2Na : Ba2+ = 1 : 1, Ba(OH)2 concentration is 0.1 mol L−1, HF concentration is 2.0 mol L−1, hydrothermal temperature is 80 °C and hydrothermal time is 2.0 h. The self-assembly mechanism of the spherical secondary structure was revealed from the perspective of crystal nucleation and growth, and the important role of EDTA in the spherical BaF2 formation is explained.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...