Benchtop X-ray fluorescence imaging as a tool to study gold nanoparticle penetration in 3D cancer spheroids
Abstract
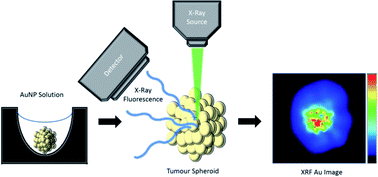
The use of nanomaterials to improve medical diagnostics and therapeutics has been rapidly increasing. Among these materials are gold nanoparticles, which can be functionalized to target specific cells, acting as nanovectors for drug delivery, enhanced contrast agents as well as other targeted therapies. Au nanoparticles are very useful as they selectively accumulate in tumour sites due to the enhanced permeability-retention effect. There is however little information about the spatial distribution of the nanoparticles within tumours, which might hinder efficient therapies. In this study, X-ray fluorescence was used to investigate the diffusion of gold nanoparticles in cancer cell spheroids mimicking true tumour growth. Functionalization of the nanoparticles has the effect of allowing better diffusion into and out of the spheroid, while those nanoparticles that are only partially covered rapidly formed aggregates. This clustering led to size exclusion during transport within the tumour, changing its distribution profile while greatly increasing the nanoparticle concentration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...