Effect of hydrothermal aging temperature on a Cu-SSZ-13/H-SAPO-34 composite for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3†
Abstract
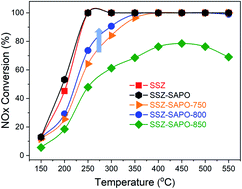
Cu-SSZ-13 suffers activity loss after hydrothermal treatment at high temperatures, particularly above 850 °C. The stability of Cu-SSZ-13 can be enhanced by compositing with H-SAPO-34. This work investigates the effect of aging temperature on the composites. For the structure, the extra-framework P in H-SAPO-34 migrates and interacts with the Al in Cu-SSZ-13, forming a new framework P–Al bond. This interaction is enhanced with the increment of the aging temperature. For the cupric sites, the aging at 750 °C results in the agglomeration of Cu2+ ions to CuO. However, the sample aged at 800 °C exhibits higher activities than that aged at 750 °C, which might be attributed to the increased formation of framework P–Al bonds promoting the redispersion of CuO to Cu2+ ions. The composite suffers severe deactivation due to the significant loss of Cu2+ ions after aging at 850 °C.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...