Vancomycin conjugated iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic targeting and efficient capture of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria
Abstract
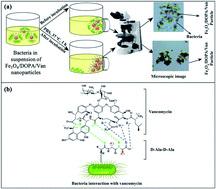
Drug conjugated iron oxide magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles are of great interest in the field of biomedicine. In this study, vancomycin (Van) conjugated magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles were envisioned to capture and inhibit the growth of bacteria. Hydrophobic Fe3O4 nanoparticles were synthesized by using co-precipitation of ferrous (Fe2+) and ferric (Fe3+) ions following a surface modification step with oleic acid as stabilizers. Thereafter, a ligand exchange technique was employed to displace oleic acid with hydrophilic dopamine (DOPA) molecules which have a catechol group for anchoring to the iron oxide surface to prepare water dispersible nanoparticles. The surface of the resulting Fe3O4/DOPA nanoparticles contains amino (–NH2) groups that are conjugated with vancomycin via a coupling reaction between the –NH2 group of dopamine and the –COOH group of vancomycin. The prepared vancomycin conjugated Fe3O4/DOPA nanoparticles were named Fe3O4/DOPA/Van and exhibited a magnetic response to an external magnetic field due to the presence of magnetite Fe3O4 in the core. The Fe3O4/DOPA/Van nanoparticles showed bactericidal activity against both Gram positive Bacillus subtilis (B. subtilis) and Streptococcus and Gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli). Maximum inhibition zones of 22 mm, 19 mm and 18 mm were found against B. subtilis, Streptococcus and E. coli respectively. Most importantly, the vancomycin conjugated nanoparticles were effectively bound to the cell wall of the bacteria, promoting bacterial separation and growth inhibition. Therefore, the prepared Fe3O4/DOPA/Van nanoparticles can be promising for effective bacterial separation and killing in the dispersion media.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...