Development of pyrazoline-based derivatives as aminopeptidase N inhibitors to overcome cancer invasion and metastasis†
Abstract
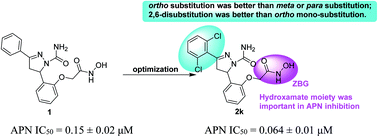
Aminopeptidase N is considered as a promising anti-tumor target due to its role in tumor invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. In this report, a new series of pyrazoline-based derivatives were designed, synthesized and evaluated for biological activities. The structure–activity relationships of these pyrazoline-based derivatives were also discussed in detail. Among them, compound 2k, with 2,6-dichloro substitution, showed the best APN inhibitory activity, of which the IC50 value was two orders of magnitude lower than that of the positive control bestatin. At the same concentration of 100 μM, the in vitro anti-invasion activity of compound 2k was also significantly better than that of bestatin. Moreover, compound 2k could effectively prevent the pulmonary metastasis of mice H22 hepatoma cells in vivo, supporting its further research and development as an antitumor agent.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...