Template-assisted synthesis of Ag/AgCl hollow microcubes and their composition-dependent photocatalytic activity for the degradation of phenol†
Abstract
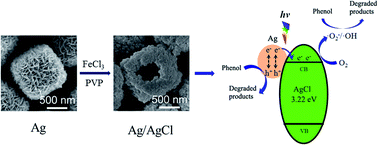
Plasmonic photocatalysts with hollow structures and tunable composition exhibit significant advantages due to their high efficiency in light collection and effective charge transfer across the tight contact heterojunction interface. Herein, hollow Ag/AgCl microcubes were developed by treating nanosheet-assembled hollow Ag microcubes with FeCl3, where a part of Ag at the interface could be in situ transformed and oxidized into AgCl. Equally, by adjusting the concentration of Fe3+ ions, Ag/AgCl hollow microcubes with different compositions could be easily achieved. Electron transfer was favored by a lot of tiny Ag/AgCl heterojunctions induced by the in situ oxidation of the multicrystalline Ag hollow microcube template containing a number of grain boundaries. The designed hollow Ag/AgCl microcubes exhibited strong visible-light adsorption owing to the surface plasmon resonance effect of Ag nanoparticles, in addition to the multiple light-reflections inside the hollow structure. The as-obtained products were then used as visible-light photocatalysts, where the results indicated that 91.6% of phenol was degraded within 150 min under visible light by the as-obtained sample with a Ag to AgCl ratio of 1 : 3. The superior visible-light photocatalytic activity resulted from the enhancement of the visible light-harvesting and the efficient charge separation at the Ag and AgCl contact interfaces.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...