Rigid 3D-spiro chromanone as a crux for efficient antimicrobial agents: synthesis, biological and computational evaluation†
Abstract
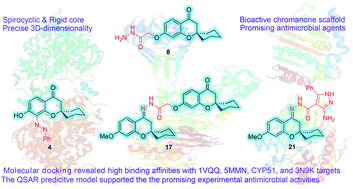
The development of new and effective antimicrobial agents with novel chemical skeletons and working mechanisms is highly desirable due to the increased number of resistant microbes. Different new compounds based upon a 3D-spiro chromanone scaffold such as Mannich bases 2 and 3 in addition to azo dye 4 were synthesized. Besides, the condensation reactions of the hydrazide-spiro chromanone 8 with different ketonic reagents led to the synthesis of pyrazoles (9 & 10) and anils (11 & 13). Moreover, the methoxyl substituted spiro chromanone 14 was condensed with different hydrazines and hydrazides to give the corresponding hydrazones 15–18 in up to 85% yields. The condensation of the hydrazone 18 with salicylaldehyde yielded coumarinyl spiro chromanone 19 in an excellent yield, whereas its reaction with benzaldehyde followed by hydrazine afforded aminopyrazole derivative 21 in 82% yield. The antimicrobial evaluation suggested that hydrazide 8 has a substantial activity against different microbes (S. aureus: D = 22 mm, MIC = 1.64 μM; E. coli: D = 19 mm, MIC = 1.64 μM; C. albicans: D = 20 mm, MIC = 6.57 μM). Moreover, promising antimicrobial activities were observed for azo dye 4 (D = 13–19 mm, MIC = 5.95–11.89 μM), hydrazone 17 (D = 17–23 mm, MIC = 1.88–3.75 μM), and aminopyrazole 21 (D = 14–19 mm, MIC = 2.24–8.98 μM). The molecular docking revealed that compounds 4, 8, 17, and 21 had good to high binding affinities with different microbial targets such as penicillin-binding proteins (−7.4 to −9.9 kcal), DNA gyrase (−7.8 to −9.0 kcal), lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (−8.2 to −11.2 kcal), and exo-beta-1,3-glucanase (−8.2 to −11.9 kcal). The QSAR analysis ascertained a good correlation between the antimicrobial activity of 3D-spiro chromanone derivatives and their structural and/or physicochemical parameters.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...