Study of deposition parameters and growth kinetics of ZnO deposited by aerosol assisted chemical vapor deposition†
Abstract
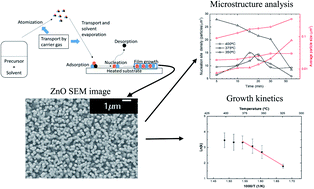
Aerosol-assisted Chemical Vapor Deposition (AACVD) is a thermally activated CVD technique that uses micro-droplets as deposition precursors. An AACVD system with a custom-designed reaction chamber has been implemented to grow ZnO thin films using zinc chloride as a precursor. The present work aims to study the impact of the deposition parameters on the thin film, as well as the microstructure evolution and growth kinetics. Aerosol flow has an effect on the density of nucleation sites and on the grain size. The temperature affects the morphology of the grown ZnO, showing a preferential orientation along the c-axis for 350 °C, 375 °C and 400 °C substrate temperatures. The microstructural evolution and the growth kinetics are also presented. A different evolution behavior has been observed for 350 °C, where nucleation site density is the highest at the early stages and it decreases over time in contrast with the cases of 375 °C and 400 °C, where there is an initial increase and a subsequent decrease. The activation energy of the chemical reaction is 1.06 eV. The optical characterization of the material has been performed through reflection measurements showing a relationship between the spectrum and the ZnO film thickness. The electrical characterization has been done by means of an interdigital capacitor, with which it is possible to measure the grain and grain boundary resistance of the material. Both resistances are of the order of 105–106 Ω.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...