UV-enhanced nano-nickel ferrite-activated peroxymonosulfate for the degradation of chlortetracycline hydrochloride in aqueous solution
Abstract
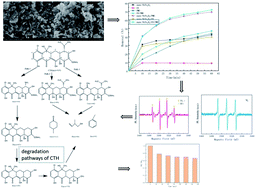
In this study, nano-nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) was successfully prepared by hydrothermal synthesis and applied to the oxidative removal of chlortetracycline hydrochloride (CTH) in the presence of ultraviolet radiation (UV) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS). Several characterization methods were used to reveal the morphology and surface properties of nano-NiFe2O4, including X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Fourier transform infrared absorption (FTIR) spectroscopy. The removal efficiency of CTH, the factors affecting the reaction process and the reaction mechanism of PMS activated by UV combined with nano-NiFe2O4 (UV + nano-NiFe2O4/PMS) in aqueous solution were systematically studied. The results showed that the UV + nano-NiFe2O4/PMS system led to a higher removal efficiency of CTH than other parallel systems. The results also showed that the CTH removal efficiency was enhanced under optimal conditions ([nano-NiFe2O4] = 1 g L−1, [PMS] = 1 g L−1, [UV wavelength] = 254 nm and [pH] = 11) and that a removal efficiency of 96.98% could be achieved after 60 min. In addition, the influence of the PMS concentration, CTH concentration, dosage of added nano-NiFe2O4 and pH on the PMS activation efficiency and CTH oxidative degradation effect was studied. Inorganic anions such as Cl−, HCO3−, CO32− and NO3− increased the removal efficiency of CTH by 21.29%, 27.17%, 25.32% and 5.96% respectively, while H2PO4− inhibited CTH removal, and the removal efficiency of CTH decreased 6.08% after 60 min. Free radical identification tests detected SO4−˙, OH˙ and 1O2 and showed that these species participated in the degradation reaction of CTH. The results of LC-MS and TOC analysis showed that CTH was degraded in the UV + nano-NiFe2O4/PMS system through hydroxylation, demethylation, deamination, and dehydration reaction and finally mineralized into CO2. These findings confirmed that nano-NiFe2O4 is a green and efficient heterogeneous catalyst for activation of PMS and demonstrates potential applicability in the treatment of antibiotic wastewater.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...