Role of oxide support in Ni based catalysts for CO2 methanation
Abstract
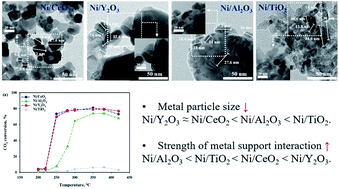
The CO2 methanation reaction of reduced and unreduced Ni based CeO2, Al2O3, TiO2 and Y2O3 supported catalysts was investigated. The Ni/CeO2 and Ni/Y2O3 catalysts exhibited similar CO2 conversions at all reaction temperatures. The catalysts were studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD), H2 chemisorption, H2 temperature-programmed reduction (TPR), and in situ diffuse reflection infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS); the results suggested that the reducibility of both metal and support at low temperature, strong metal support interaction and small Ni particle size are important factors for low-temperature CO2 methanation. Based on the DRIFT studies, the difference in the CO2 adsorption properties and reaction pathway depending on the reduced and unreduced Ni based supported catalysts was discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...