Preparation, characterization serpentine-loaded hydroxyapatite and its simultaneous removal performance for fluoride, iron and manganese
Abstract
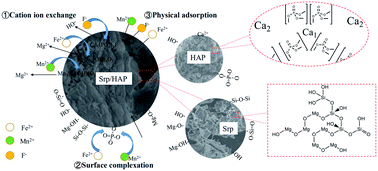
Aiming at the problem of excessive fluorine, iron, and manganese pollution in groundwater in mining areas, a serpentine-loaded hydroxyapatite (Srp/HAP) composite adsorbent was prepared by wet chemical coprecipitation. The preparation conditions of the Srp/HAP composite adsorbent were explored, Srp/HAP was microscopically characterized, and the adsorption performance and adsorption mechanism of the Srp/HAP composite adsorbent for F−, Fe2+ and Mn2+ were analyzed. The results showed that the optimal preparation conditions for the composite particles were as follows: solid–liquid ratio of Srp to calcium nitrate solution 20%, aging time 20 h, calcination temperature 180 °C, and calcination time 90 min. Compact Srp/HAP composite adsorbent particles were successfully prepared, and both the lamellar crimp structure of the Srp surface and the problem of HAP surface agglomeration were resolved. After loading, the specific surface area and pore volume of the particles significantly increased, and the surface pore structure improved, which is conducive to the simultaneous adsorption and removal of fluorine, iron and manganese. The optimal reaction conditions for Srp/HAP treatment of composite water samples with F−, Fe2+ and Mn2+ mass concentrations of 5 mg L−1, 20 mg L−1 and 5 mg L−1, respectively, are as follows: dosage of Srp/HAP 3 g L−1, pH 7, temperature 35 °C, and reaction time 150 min. Under these conditions, the removal rates of F−, Fe2+ and Mn2+ were 98.6%, 99.9% and 99.8%, respectively. The quasi-second-order kinetic model and Langmuir isothermal adsorption model described the adsorption process of F−, Fe2+ and Mn2+ by the composite particles well. The adsorption process includes both surface physical adsorption and chemical adsorption. Chemical adsorption is mainly characterized by ion exchange and surface complexation. The Srp/HAP composite particles can be used as an excellent adsorbent for the treatment of groundwater containing fluorine, iron and manganese ions in mining areas.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...