Natural coumarins as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents supported by docking analysis†
Abstract
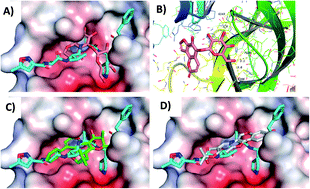
COVID-19 is a global pandemic first identified in China, causing severe acute respiratory syndrome. One of the therapeutic strategies for combating viral infections is the search for viral spike proteins as attachment inhibitors among natural compounds using molecular docking. This review aims at shedding light on the antiviral potential of natural products belonging to the natural-products class of coumarins up to 2020. Moreover, all these compounds were filtered based on ADME analysis to determine their physicochemical properties, and the best 74 compounds were selected. Using virtual-screening methods, the selected compounds were investigated for potential inhibition of viral main protease (Mpro), viral methyltransferase (nsp16/10 complex), viral recognition binding domain (RBD) of S-protein, and human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), which is the human receptor for viral S-protein targets, using molecular-docking studies. Promising potential results against SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) and methyltransferase (nsp16) are presented.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Coronavirus articles - free to access collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...