Release of methane from nanochannels through displacement using CO2
Abstract
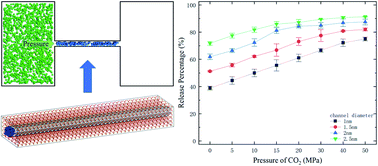
In this work, we investigate the release of methane in quartz nanochannels through the method of displacement using carbon dioxide. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and theoretical analysis are performed to obtain the release percentage of methane for nanochannels of various diameters. It is found that both the pressure of CO2 and the channel size affect the release percentage of methane, which increases with increasing pressure of CO2 and channel diameter. Without CO2, the majority of methane molecules are adsorbed by the channel surface. When CO2 is injected into the channel, CO2 molecules replace many methane molecules due to the relatively strong molecular interactions between CO2 and the channel, which leads to the desorption of methane, reduces the energy barrier for the transport of methane, and consequently increases the release rate. Theoretical predictions using the kinetic energy of methane and the energy barrier inside the channel are also conducted, which are in good agreement with the MD simulations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...