Peroxymonosulfate activation by tea residue biochar loaded with Fe3O4 for the degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride: performance and reaction mechanism
Abstract
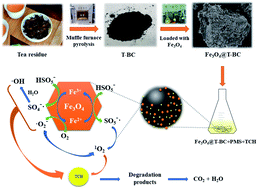
The recycling of agricultural and food waste is an effective way to reduce resource waste and ameliorate the shortage of natural resources. The treatment of antibiotic wastewater is a current research hotspot. In this study, waste tea residue was used as a raw material to prepare biochar (T-BC) and loaded with Fe3O4 as a catalyst to activate peroxymonosulfate (PMS) for oxidative degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride (TCH). Analysis techniques such as BET, SEM, XRD, FT-IR, XPS and VSM indicated that the heterogeneous catalyst (Fe3O4@T-BC) with good surface properties and magnetic properties was successfully prepared. The results of batch-scale experiments illustrated that when the dose of the Fe3O4@T-BC catalyst was 1 g L−1, the concentration of PMS was 1 g L−1, and the initial pH was 7, the degradation rate of TCH with a concentration of 50 mg L−1 reached 97.89% after 60 minutes of reaction. When the initial pH was 11, the degradation rate of TCH reached 99.86%. After the catalyst was recycled four times using an external magnet, the degradation rate of TCH could still reach 71.32%. The data of removal of TCH could be best fitted by a pseudo-first-order model. The analysis of the degradation mechanism through a free radical quenching experiment and EPR analysis, as well as the exploration of TCH intermediate products and reaction paths through the LC-MS method, all confirmed that the Fe3O4@T-BC prepared by this method is expected to become a cost-effective and environmentally friendly heterogeneous catalyst for activating persulfate degradation of tetracycline antibiotics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...