IQF characterization of a cathepsin B-responsive nanoprobe for report of differentiation of HL60 cells into macrophages†
Abstract
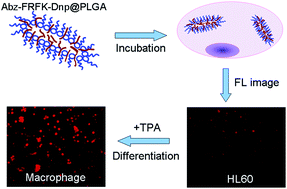
Tracking of in vivo fates of exogenous cell transplants in terms of viability, migration, directional differentiation and function delivery by a suitable method of medical imaging is of great significance in the development and application of various cell therapies. In this contribution directional differentiation of HL60 cells into macrophages and granulocytes, and a difference in the associated expression level of cathepsin B (Cat B) among the parent and daughter cells is used as a model to guide and evaluate the development of a Cat B-responsive Abz-FRFK-Dnp@PLGA nanoprobe for an optical report of the differentiation process. A well-documented internally quenched fluorescence (IQF) pair coupled with a peptide substrate FRFK of Cat B was synthesized and imbedded in PLGA to form the nanoprobe. The nanoprobe is resistant to leakage when dispersed in water for 10 days. Degradation of the nanoprobe is dominated by Cat B. HL60 cells were then labelled with the Abz-FRFK-Dnp@PLGA nanoprobe to track the differentiation process. Differentiation of labelled HL60 cells into macrophages exhibited a significantly higher fluorescence relative to the granulocytes or the labelled parent cells. The fluorescence difference allows the differentiation process to be followed. The established characterization and assessment procedure is to be used for the development and evaluation of nanoprobes for other imaging modalities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...