Enzymatic preparation of phytosterol esters with fatty acids from high-oleic sunflower seed oil using response surface methodology†
Abstract
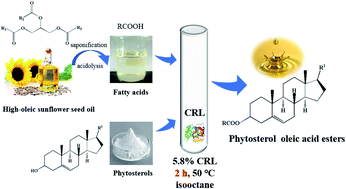
Phytosterol esters are functional compounds that can effectively reduce plasma cholesterol concentration, and have wide applications in the food industry. In this study, a simple and efficient enzymatic method was successfully applied to synthesize phytosterol oleic acid esters with fatty acids from high-oleic sunflower seed oil. Among the tested lipases, Candida rugosa lipase (CRL) exhibited higher catalytic activity in the esterification of phytosterols with fatty acids (oleic acid 84%) from high-oleic sunflower seed oil. Box–Behnken design and response surface methodology were used to investigate the influence of reaction factors on the conversion of phytosterols. The maximum conversion of phytosterols (96.8%) and yield of phytosterol esters (92%) could be obtained under optimal conditions: reaction temperature 50 °C, a molar ratio of phytosterols to fatty acids at 1 : 2.3, enzyme loading of 5.8%, isooctane volume of 2 mL and reaction time of 2 h. It was noteworthy that this enzymatic esterification method indeed expended a much shorter reaction time (2 h) than that observed in previous reports. In general, the enzymatic preparation of phytosterol oleic acid esters with fatty acids from high-oleic sunflower seed oil will be a simple and rapid method for producing unsaturated fatty acid esters of phytosterol with both higher oil solubility and oxidative stability, which is beneficial as functional food ingredients.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...