Facile synthesis of antibiotic-functionalized gold nanoparticles for colorimetric bacterial detection†
Abstract
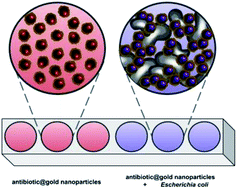
The development of quick and efficient methods for the detection of pathogenic bacteria is urgently needed for the diagnosis of infectious diseases and the control of microbiological contamination in global waterways, potable water sources and the food industry. This contribution will describe the synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their conjugation to broad spectrum, polypeptide and β-lactam antibiotics that function as both reducing agents and surface protectants (ATB@AuNP). Nanoparticle colloids examined using transmission electron microscopy are generally spherical in shape and range from 2–50 nm in size. Dynamic light scattering and infrared spectroscopy were also used to confirm encapsulation of the AuNP surface by antibiotic molecules. ATB@AuNP were then used to detect 3 common pathogenic bacterial species: Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Escherichia coli. The colour of the AuNP colloid was monitored visually and using UV-visible spectroscopy. A red shift of the UV visible absorbance and a visible colour change following introduction of each pathogen is indicative of ATB binding to the bacteria surface, ascribed to AuNP agglomeration. This work demonstrates that ATB@AuNP may be an efficient and high throughput tool for the rapid detection of common bacterial contaminants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...