Nucleation of diamond films on heterogeneous substrates: a review
Abstract
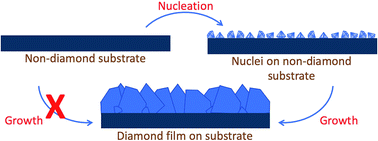
Diamond thin films are known to have properties similar to bulk diamond and have applications in both industry and fundamental studies in academia. The high surface energy of diamond makes it extremely difficult to grow diamond films on foreign substrates. Hence, to grow diamond films on non-diamond substrates, a nucleation step is needed. In this review various techniques used for diamond nucleation/seeding will be discussed. At present electrostatic seeding by diamond nanoparticles is the most commonly used seeding technique for nanocrystalline growth. In this technique the substrate is dipped in a nanodiamond solution to form a mono layer of diamond seeds. These seeds when exposed to appropriate conditions grow to form diamond layers. This technique is suitable for most substrates. For heteroepitaxial growth, bias enhanced nucleation is the primary technique. In this technique the substrate is biased to form diamond nuclei in the initial stages of growth. This technique can be used for any conducting flat surface. For growth on ceramics, polishing by diamond grit or electrostatic seeding can be used. Polishing the ceramics with diamond powder leaves small diamond particles embedded in the substrate. These small particles then act as seeds for subsequent diamond growth. Apart from these techniques, chemical nucleation, interlayer driven nucleation and mixed techniques have been discussed. The advantages and disadvantages of individual techniques have also been discussed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 Reviews in RSC Advances


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...