Reversible and irreversible membrane fouling in hollow-fiber UF membranes filtering surface water: effects of ozone/powdered activated carbon treatment†
Abstract
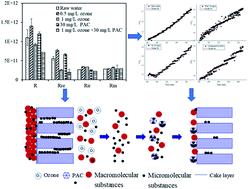
This study investigated the reversible and irreversible membrane fouling behavior of micro polluted water by ozone/powdered activated carbon (PAC)/ultrafiltration treatment. The results indicated that PAC mainly adsorbed low-molecular weight organics and reduced the irreversible fouling resistance in ultrafiltration, while there existed a threshold PAC dosage for total and reversible fouling resistance alleviation. Ozone at low doses exerted little effect on membrane fouling alleviation, while higher doses controlled total and reversible fouling by reducing macromolecular biopolymers and humic-like substances. Combined ozone and PAC pretreatment had greater effects on both reversible and irreversible fouling reduction than individual PAC and ozone treatment, demonstrating synergistic effects in the reduction of organic content in the feed water, including macromolecular biopolymers, humic-like, low-molecular weight neutral and building blocks. Backwashing and chemical cleaning analysis revealed that biopolymers and humic-like substances were the main organics that caused hydraulic reversible fouling, whereas low-molecular organics of building blocks and neutral, as well as humic-like substances were the main components that caused hydraulic irreversible fouling. Combined ozone and PAC treatment not only improved the backwashing efficiency but also reduced the membrane fouling during backwashing, as well as reversible and irreversible fouling. The cake layer formation and standard pore blocking were the major mechanisms for ultrafiltration membrane fouling, of which standard pore blocking exerted more important effects in the membrane fouling formation and alleviation by individual and combined PAC and ozone treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...