Discovery of quinolone derivatives as antimycobacterial agents†
Abstract
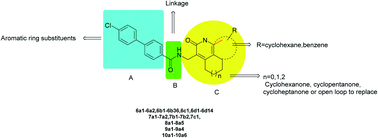
Tuberculosis (TB), an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis), is an important public health issue. Current first-line drugs administered to TB patients have been in use for over 40 years, whereas second-line drugs display strong side effects and poor compliance. Additionally, designing effective regimens to treat patients infected with multi- and extremely-drug-resistant (MDR and XDR) strains of TB is challenging. In this report, we screened our compound library and identified compound 1 with antituberculosis activity and a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) against M. tuberculosis of 20 μg mL−1. Structure optimization and the structure–activity relationship of 1 as the lead compound enabled the design and synthesis of a series of quinolone derivatives, 6a1–6a2, 6b1–6b36, 6c1, 6d1–6d14, 7a1–7a2, 7b1–7b2, 7c1, 8a1–8a5, 9a1–9a4 and 10a1–10a6. These compounds were evaluated in vitro for anti-tubercular activity against the M. tuberculosis H37Rv strain. Among them, compounds 6b6, 6b12 and 6b21 exhibited MIC values in the range of 1.2–3 μg mL−1 and showed excellent activity against the tested MDR-TB strain (MIC: 3, 2.9 and 0.9 μg mL−1, respectively). All three compounds were non-toxic toward A549 and Vero cells (>100 and >50 μg mL−1, respectively). In addition, an antibacterial spectrum test carried out using compound 6b21 showed that this compound specifically inhibits M. tuberculosis. These can serve as a new starting point for the development of anti-TB agents with therapeutic potential.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...