Ultrasound-assisted enzymatic extraction of hydroxy-sanshool compounds from the hydrodistillation residue of two Sichuan peppers: optimization, quantification and pungent taste contribution evaluation
Abstract
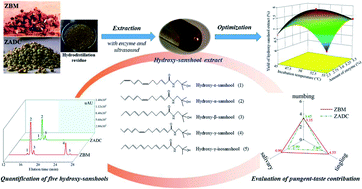
Hydroxy-sanshool compounds were extracted from the hydrodistillation residue of Z. bungeanum Maxim. pericarp (ZBM) and Z. armatum DC. pericarp (ZADC) by using ethanol–water extraction and extractions assisted with (i) enzymes, (ii) ultrasound, and (iii) enzymes and ultrasound. The yields of the hydroxy-sanshool extracts under these four extraction conditions were calculated and compared. The ultrasound-assisted enzymatic extraction was then optimized based on a Box–Behnken design. Furthermore, five hydroxy-sanshool compounds in the extracts were quantified and their pungent taste contribution value (PCV) was calculated. Oral sensory evaluation was finally performed. Compared with that of the hydroxy-sanshool extracted with ethanol–water, the yields of the samples from the extraction assisted with enzymes, ultrasound, and enzymes and ultrasound increased by 4.2–7.6%, 9.3–9.8%, and 21.5–26.2%, respectively. A maximum yield of 7.87% (w/w) was achieved by using ultrasound-assisted enzymatic extraction under the optimal conditions: 3.1% (w/w) amount of enzyme, an incubation temperature of 50.3 °C, and an ultrasound irradiation power of 207 W. The PCV of hydroxy-α-sanshool, hydroxy-β-sanshool, hydroxy-γ-sanshool, hydroxy-ε-sanshool, and hydroxy-γ-isosanshool was 1153, 447, 461, 139, and 51 ml g−1 for the ZBM extract, respectively, while the PCV of these five hydroxyl-sanshools was 659 ml g−1, 575 ml g−1, not detected, 119 ml g−1, and not detected for the ZADC extract, respectively. Tingling and salivation were the main taste sensations of ZBM, whereas numbing and tingling sensations were dominant in ZADC.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...