Flexible and wearable strain sensor based on electrospun carbon sponge/polydimethylsiloxane composite for human motion detection†
Abstract
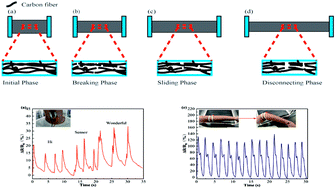
Flexible and wearable strain sensors have attracted considerable attention due to their potential applications in human motion detection. In this work, the as-fabricated strain sensor was obtained by encapsulation of electrospun carbon sponge (CS) with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). The formation mechanism of the self-assembled sponge has been explored. Meanwhile, the piezoresistive properties and the strain sensing mechanism of the CS/PDMS sensor were investigated. The results showed that the as-fabricated CS/PDMS sensor had high piezoresistive sensibility with a maximum gauge factor up to 130.49, superior stability and fast response to various cyclic loading with a tensile strain from 0% up to 40% and a tensile speed range of 2–18 mm min−1. Finally, all the superior performances endow the sensor with abilities to precisely detect pronunciation, human palm motion, wrist joint motion, elbow joint motion, and finger motion in real-time. These results indicate that the strain sensor based on the CS/PDMS could have promising applications in flexible and wearable devices for human motion detection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...