Rapid structural regulation, apatite-inducing mechanism and in vivo investigation of microwave-assisted hydrothermally treated titania coating†
Abstract
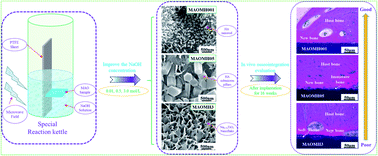
Owing to the poor bioactivity of microarc oxidation (MAO) coating and the rapid activation ability of the microwave hydrothermal (MH) technique, MH treatment was applied to optimize the in vivo interface status between MAO-treated titanium and bone. In this study, consequently, new outermost layers were prepared using hydroxyapatite (HA) nanorods, HA submicron pillars or sodium titanate nanosheets. The results revealed that the NaOH concentration significantly influenced the surface structure and phase constitution of the MAO samples. Moreover, on enhancing the NaOH concentration, the number of HA phases was decreased. Further, the influence of the NaOH concentration on the interfacial bonding strength was insignificant for concentrations ≤0.5 mol L−1. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis showed that the induction of apatite was accompanied by the dissolution of the HA crystals and there was excellent crystallographic matching with the HA crystals. The in vitro and in vivo analyses revealed that the MH-treated MAO sample with the HA nanorods possessed superior apatite-formation ability and osseointegration, including a small amount of soft tissue and optimal bone–implant interfacial bonding force, thus signifying strong potential for the optimization of the bone–implant interfacial status.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...