The pH-triggered drug release and simultaneous carrier decomposition of effervescent SiO2–drug–Na2CO3 composite nanoparticles: to improve the antitumor activity of hydrophobic drugs
Abstract
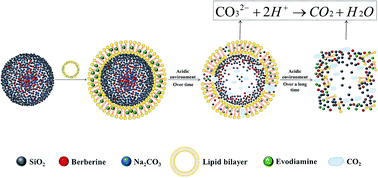
To achieve a better release effect of hydrophobic drugs and spontaneous nanocarrier disintegration by dissolution as well as the CO2 production of Na2CO3 further, improving the therapeutic effect of hydrophobic drugs, and thereby avoiding the accumulation of the nanocarrier in vivo to produce organ toxicity, effervescent SiO2–drug–Na2CO3 composite nanoparticles (ESNs) were prepared in this study using a tetraethyl orthosilicate hydrolysis method. Sodium carbonate was used as the effervescent disintegrant to respond to the acidic microenvironment of the tumor. The properties of ESNs were assessed and TEM images were taken to verify the self-disintegration characteristics of nanocarrier materials. The in vitro anticancer efficacy of ESNs was evaluated in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. ESNs loaded with hydrophobic drugs were successfully constructed, and showed high entrapment efficiency and drug loading. The nanocarrier successfully achieved self-disintegration in a PBS environment of pH value at 5.0, and showed excellent antitumor effect in vitro. ESNs can effectively load hydrophobic drugs and achieve self-disintegration, while avoiding toxicity from the accumulation of the nanocarrier. These results suggest that ESNs are a promising drug delivery system capable of maximizing the anticancer therapeutic efficacy and minimizing the systemic toxicity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...