Antitumor substitution-inert polynuclear platinum complexes stabilize G-quadruplex DNA and suppress G-quadruplex-mediated gene expression†
Abstract
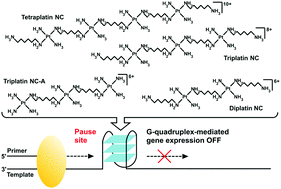
DNA G-quadruplex (G4) structures formed in the telomeric and promoter regions represent attractive drug targets for anticancer therapy. Thus, much effort has been devoted to the development of a variety of G4-binding ligands, mostly based on rigid planar structures. Here, we investigated the efficacy of inherently flexible anticancer substitution-inert polynuclear platinum(II) complexes (SI-PPCs) to stabilize DNA G4s and terminate DNA polymerization on templates containing G4-forming sequences. Conventional DNA polymerase primer extension assay, fluorescence melting studies, fluorescence indicator displacement assay and circular dichroism spectroscopy revealed that SI-PPCs can stabilize DNA G4s and terminate DNA polymerization on templates containing G4-forming sequences although they lack structural properties of traditional G4 binders. Despite that the selectivity for G4 DNA over double-stranded DNA was somewhat lower than that observed for some traditional G4-binding ligands, it was notable that one of the investigated SI-PPCs, anticancer Triplatin NC, reduced the expression of G4-regulated genes c-myc and c-kit in human embryonic kidney cells. These results demonstrate that the overall biological activity of SI-PPCs can also involve interactions of SI-PPCs with different cellular targets acting as multi-target-directed compounds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...