Facile synthesis of GalNAc monomers and block polycations for hepatocyte gene delivery†
Abstract
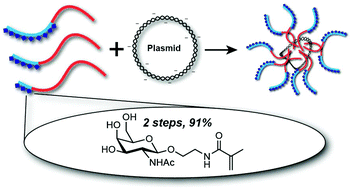
The ability to design liver-targeted polymers for nucleic acid delivery vehicles is plagued with difficulties ranging from polymer-mediated cellular toxicity to challenges in synthesizing monomers that enable facile cell-specific polymeric gene delivery vehicles. Herein is presented an improved synthetic route to a N-acetyl-D-galactosamine (GalNAc)-derived monomer (two steps, 91% overall yield) and its incorporation into a library of nine diblock co-polymers with 2-aminoethylmethacrylamide (AEMA) and two end-group functionalized AEMA homopolymers. These polymers were complexed with plasmid DNA (pDNA) into polyplexes and evaluated for the toxicity, uptake and transfection efficiency against cultured hepatocytes (HepG2) at N/P ratios of 2.5, 5, and 10. All polyplexes showed a range of cell survivability between 60–90%, an improvement over JetPEI, a commercial transfection reagent, when dosed at standard concentrations. Although GalNAc block length does not play a significant role in cellular uptake of Cy-5 labeled pDNA, it has a heavy influence on the transfection efficiency of luciferase-encoded pDNA where longer GalNAc block lengths give rise to higher transfection efficiencies. Overall, this work demonstrates a greatly improved route to GalNAc monomer synthesis, which that can be incorporated into polymers that target hepatocytes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...