Synthesis of well-defined di- and triblock acrylic copolymers consisting of hard poly(dicyclopentanyl acrylate) and soft poly(alkyl acrylate) segments by organocatalyzed group transfer polymerization and their glass transition behavior†
Abstract
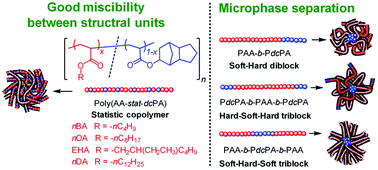
A series of well-defined di- and triblock acrylic copolymers consisting of hard poly(dicyclopentanyl acrylate) (PdcPA) and soft poly(alkyl acrylate) (PAA) blocks are synthesized by the N-(trimethylsilyl)bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (Me3SiNTf2) catalyzed group transfer polymerization (GTP) of dicyclopentanyl acrylate (dcPA) and alkyl acrylate (AA) including n-butyl acrylate (nBA), n-octylacrylate (nOA), 2-ethylhexyl acrylate (EHA), and n-dodecyl acrylate (nDA). The distribution of the monomeric units of the copolymers is controlled through the addition sequence of the comonomers and by the used initiator. In greater detail, the mixed addition of AA and dcPA using the monofunctional 1-methoxy-1-triisopropylsiloxy-2-methylpropene (MTSiPr) as the initiator produces the statistical poly[(alkyl acrylate)-stat-(dicyclopentanyl acrylate)] (Poly(AA-stat-dcPA)), the sequential addition of AA and then dcPA using MTSiPr as an initiator produces the AB-type hard–soft diblock poly(alkyl acrylate)-block-poly(dicyclopentanyl acrylate) (PAA-b-PdcPA), the sequential addition of AA and then dcPA using the bifunctional 1,2-bis[2-methyl-1-(triisopropylsiloxy)prop-1-enyloxy]ethane (MTSiPr2) as the initiator affords the ABA-type hard–soft–hard triblock poly(dicyclopentanyl acrylate)-block-poly(alkyl acrylate)-block-poly(dicyclopentanyl acrylate) (PdcPA-b-PAA-b-PdcPA), and the reverse addition of the two monomers using MTSiPr2 affords the soft–hard–soft BAB-type triblock poly(alkyl acrylate)-block-poly(dicyclopentanyl acrylate)-block-poly(alkyl acrylate) (PAA-b-PdcPA-b-PAA). The formation of the statistical and block copolymers has been confirmed by 1H NMR spectroscopy and size exclusion chromatography (SEC) measurements. Afterwards, the glass transition behavior of the resulting copolymers is analyzed by both differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and rheometry. A detailed discussion of this part is presented in the following sections.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...