A high-yielding solid-phase total synthesis of daptomycin using a Fmoc SPPS stable kynurenine synthon†
Abstract
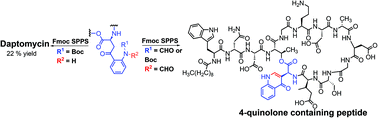
A high-yielding total synthesis of daptomycin, an important clinical antibiotic, is described. Key to the development of this synthesis was the elucidation of a Camps cyclization reaction that occurs in the solid-phase when conventionally used kynurenine (Kyn) synthons, such as Fmoc-L-Kyn(Boc,CHO)-OH and Fmoc-L-Kyn(CHO,CHO)-OH, are exposed to 20% 2-methylpiperidine (2MP)/DMF. During the synthesis of daptomycin, this side reaction was accompanied by intractable peptide decomposition, which resulted in a low yield of Dap and a 4-quinolone containing peptide. The Camps cyclization was found to occur in solution when Boc-L-Kyn(Boc,CHO)-Ot-Bu and Boc-L-Kyn(CHO,CHO)-OMe were exposed to 20% 2MP/DMF giving the corresponding 4-quinolone amino acid. In contrast, Boc-L-Kyn(CHO)-OMe was stable under these conditions, demonstrating that removing one of the electron withdrawing groups from the aforementioned building blocks prevents enolization in 2MP/DMF. Hence, a new synthesis of daptomycin was developed using Fmoc-L-Kyn(Boc)-OH, which is prepared in two steps from Fmoc-L-Trp(Boc)-OH, that proceeded with an unprecedented 22% overall yield. The simplicity and efficiency of this synthesis will facilitate the preparation of analogs of daptomycin. In addition, the elucidation of this side reaction will simplify preparation of other Kyn-containing natural products via Fmoc SPPS.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...