Endothelial cell membrane-based biosurface for targeted delivery to acute injury: analysis of leukocyte-mediated nanoparticle transportation†
Abstract
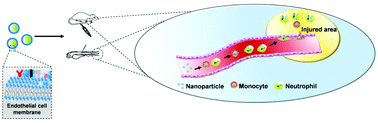
Mimicking and leveraging biological structures and materials provide important approaches to develop functional vehicles for drug delivery. Taking advantage of the affinity and adhesion between the activated endothelial cells and innate immune cells during inflammatory responses, hybrid polyester nanoparticles coated with endothelial cell membranes (EM-P) containing adhesion molecules were fabricated and their capability as vehicles to travel to the acute injury sites through leukocyte-mediated processes was investigated. The in vivo studies and quantitative analyses performed through the lung-inflammation mouse models demonstrated that the EM-Ps preferentially interacted with the neutrophils and monocytes in the circulation and the cellular membrane-based biosurface improved the nanoparticle transportation to the inflamed lung possibly via the motility of neutrophils. Utilizing the transgenic zebrafish model, the leukocyte-mediated transportation and biodistribution of EM-Ps were further visualized in real time at the whole-organism level. Endothelial membranes provided a new biosurface for developing biomimetic vehicles to allow the immune cell-mediated transportation and may enable advanced systems for active and highly efficient drug delivery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...