A numerical study on drug delivery via multiscale synergy of cellular hitchhiking onto red blood cells
Abstract
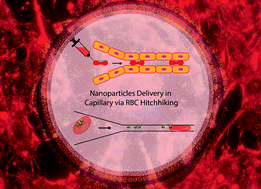
Red blood cell (RBC)-hitchhiking, in which different nanocarriers (NCs) shuttle on the erythrocyte membrane and disassociate from RBCs to the first organ downstream of the intravenous injection spot, has recently been introduced as a solution to enhance target site uptake. Several experimental studies have already approved that cellular hitchhiking onto the RBC membrane can improve the delivery of a wide range of NCs in mice, pigs, and ex vivo human lungs. In these studies, the impact of NC size, NC surface chemistry, and shear rate on the delivery process and biodistribution has been widely explored. To shed light on the underlying physics in this type of drug delivery system, we present a computational platform in the context of the lattice Boltzmann method, spring connected network, and frictional immersed boundary method. The proposed algorithm simulates nanoparticle (NP) dislodgment from the RBC surface in shear flow and biomimetic microfluidic channels. The numerical simulations are performed for various NP sizes and RBC–NP adhesion strengths. In shear flow, NP detachment increases upon increasing the shear rate. RBC–RBC interaction can also significantly boost shear-induced particle detachment. Larger NPs have a higher propensity to be disconnected from the RBC surface. The results illustrate that changing the interaction between the NPs and RBCs can control the desorption process. All the findings agree with in vivo and in vitro experimental observations. We believe that the proposed setup can be exploited as a predictive tool to estimate optimum parameters in NP-bound RBCs for better targeting procedures in tissue microvasculature.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...