Three-dimensional microspheres constructed with MoS2 nanosheets supported on multiwalled carbon nanotubes for optimized sodium storage†
Abstract
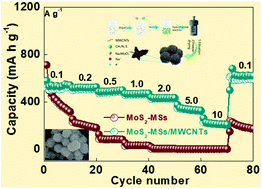
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) has been regarded as a promising anode material in the field of sodium-ion batteries (SIBs), with the advantages of high theoretical capacity and large interlayer spacings. Unfortunately, its intrinsic poor electrical conductivity and large volume changes during the sodiation/desodiation reactions still limit its practical application. To deal with this shortcoming, we built MoS2 nanosheet/multiwalled carbon nanotube (denoted as MoS2-MSs/MWCNTs) composites with a three-dimensional (3D) micro-spherical structure, assembled in situ from MoS2 nanosheets. These nanosheets are connected to each other by the MWCNTs network, which provides a highly conductive pathway for electrons/ions through interparticle and intraparticle interfaces, accelerating charge transfer and ion diffusion capabilities. More importantly, the carbon network can boost electrical conductivity and relieve structural strain. Consequently, the as-prepared MoS2-MSs/MWCNTs composite presents a high reversible specific capacity of 519 mA h g−1 at 0.1 A g−1 after 100 cycles with a capacity retention of 94.4% and excellent rate performance (227 mA h g−1 at 10 A g−1). Outstanding cycling stability was also achieved (327.1 mA h g−1 over 1000 cycles at 2 A g−1) and was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis. Our findings provide a simple and effective strategy to explore anode materials with advanced sodium storage properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...