Non-depleting reformation of immunosuppressive myeloid cells to broaden the application of anti-PD therapy†
Abstract
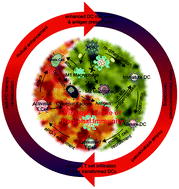
Traditional methods of depleting tumor-associated myeloid cells via chemotherapy can easily lead to the re-recruitment of them, eventually resulting in chemo-resistance and presenting obstacles in immunotherapy. Herein, we report a nano-educator (NE) that when loaded with all trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and anti-PD-1 antibodies (aPD-1) instructs myeloid cells to assist T cells towards revitalizing anti-PD-1 therapy. In vivo, ATRA converts myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) into dendritic cells (DCs), which are essential for anti-PD-1 therapy, while intervening in the polarization of macrophages. Furthermore, aPD-1-armed T cells reboot anti-tumor immunity after suppression relief, which exposes tumor-specific antigens and in turn promotes the maturation of transformed DCs. The nano-platform provides shelter for vulnerable immunomodulatory agents and durable drug release to stimulate intensive immune modulation. We established three types of tumor-bearing mice models with different myeloid cell contents to show the spatiotemporal complementarity of ATRA and aPD-1. The NE re-educates the tumor's guard to assist T cells in enhanced immunotherapy, broadening the application of aPD-1 in the treatment of anti-PD-1-resistant tumors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...