Retracted Article: Stacking of nanorings to generate nanotubes for acceleration of protein refolding†
Abstract
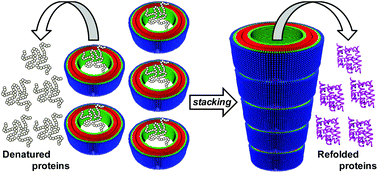
Self-assembly and photoisomerization of azobenzene-based amphiphilic molecules produced nanorings with an inner diameter of 25 nm and lengths of <40 nm. The nanorings, which consisted of a single bilayer membrane of the amphiphiles, retained their morphology in the presence of a stacking inhibitor; whereas in the absence of the inhibitor, the nanorings stacked into short nanotubes (<500 nm). When subjected to mild heat treatment, these nanotubes joined end-to-end to form nanotubes with lengths of several tens of micrometers. The nanorings and the short and long nanotubes were able to encapsulate proteins and thereby suppress aggregation induced by thermal denaturation. In addition, the nanotubes accelerated refolding of denatured proteins by encapsulating them and then releasing them into the bulk solution; refolding occurred simultaneously with release. In contrast, the nanorings did not accelerate protein refolding. Refolding efficiency increased with increasing nanotube length, indicating that the re-aggregation of the proteins was strictly inhibited by lowering the concentration of the proteins in the bulk solution as the result of the slow release from the longer nanotubes. The migration of the proteins through the long, narrow nanochannels during the release process will also contribute to refolding.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...