The application potential of machine learning and genomics for understanding natural product diversity, chemistry, and therapeutic translatability†
Abstract
Covering: up to the end of 2020.
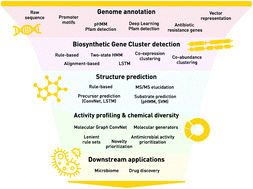
The machine learning field can be defined as the study and application of algorithms that perform classification and prediction tasks through pattern recognition instead of explicitly defined rules. Among other areas, machine learning has excelled in natural language processing. As such methods have excelled at understanding written languages (e.g. English), they are also being applied to biological problems to better understand the “genomic language”. In this review we focus on recent advances in applying machine learning to natural products and genomics, and how those advances are improving our understanding of natural product biology, chemistry, and drug discovery. We discuss machine learning applications in genome mining (identifying biosynthetic signatures in genomic data), predictions of what structures will be created from those genomic signatures, and the types of activity we might expect from those molecules. We further explore the application of these approaches to data derived from complex microbiomes, with a focus on the human microbiome. We also review challenges in leveraging machine learning approaches in the field, and how the availability of other “omics” data layers provides value. Finally, we provide insights into the challenges associated with interpreting machine learning models and the underlying biology and promises of applying machine learning to natural product drug discovery. We believe that the application of machine learning methods to natural product research is poised to accelerate the identification of new molecular entities that may be used to treat a variety of disease indications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...