Phase-dependent electrocatalytic activity of colloidally synthesized WP and α-WP2 electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction†
Abstract
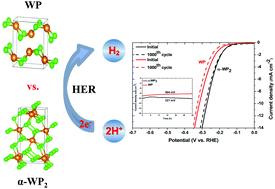
Transition metal phosphides (TMPs) have emerged as efficient non-noble electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). However, the effect of their crystal phase on the electrocatalytic activity has rarely been reported due to challenges associated with finding a facile method that allows controlled synthesis of the desired crystal phase. Herein, we report on the synthesis of the orthorhombic (WP) and monoclinic (α-WP2) phases of tungsten phosphide via colloidal synthesis coupled with annealing using tungsten hexachloride (tungsten source), trioctylphosphine (phosphorus source) and 1-octadecene (solvent and reductant). The two different phases of tungsten phosphide were obtained by simply varying the W : P precursor ratio, with the ratios of 1 : 1 and 1 : 20 resulting in the formation of WP and α-WP2, respectively. The structure and morphology of the nanoparticles were assessed using powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Experimental results revealed that the phosphorus rich α-WP2 displayed superior catalytic activity over the phosphorus poor WP in HER. The WP and α-WP2 catalysts required overpotentials of 314 and 271 mV to produce a current density of 10 mA cm−2 and Tafel slopes of 95.71 and 86.83 mV dec−1, respectively. The formation of a partial negative charge on the P atoms due to the high P content in α-WP2 allowed the positively charged H+ ions to be easily trapped on the electrocatalyst surface, resulting in an improved catalytic activity. Theoretical calculations performed using density functional theory (DFT) revealed that the high activity of α-WP2 was due to high conductivity, low hydrogen adsorption energy, low energy barrier to H–H formation, long M–P bond length and low d-band center energy. This work provides a new approach in developing highly active and stable TMPs that are suitable alternatives to Pt-based materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...