Sitosterol-fabricated chitosan nanocomplex induces apoptotic cell death through mitochondrial dysfunction in lung cancer animal model: an enhanced synergetic drug delivery system for lung cancer therapy
Abstract
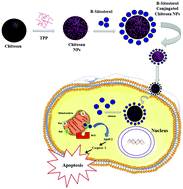
Lung carcinoma is an aggressive form of cancer, with an increasing rate of morbidity, dismal outlook, poor prognosis and limited therapeutic approaches. The present study is aimed to demonstrate the anticancer efficacy of a fabricated beta-sitosterol chitosan nanocomplex (BSC) in a human lung cancer cell line (A-549) and animal model. The nanocomplex was fabricated using beta-sitosterol and chitosan and its properties were investigated via FTIR, DLS, zeta potential, SEM, and TEM. In vitro and in vivo assessments were done employing various techniques to determine the viability and alterations in morphology of A-549 cells, and also the anti-tumor efficacy in a xenograft mice model. The outcomes revealed the apoptotic efficacy prompted by the BSC nanocomplex in both a time- and dose-dependent manner. Subsequently, AO/EB staining of the BSC nanocomplex at different concentrations led to the typical alteration in the morphology of the cells, comprising the shrinkage of cells and fragmented nucleus, resulting in apoptosis. The effect of the BSC nanocomplex on the cell cycle phase distribution and mitochondrial membrane potential was evaluated using flow cytometry. There was a notable loss in the mitochondrial membrane potential, which ultimately caused an apoptotic effect in the treated cells. Also, the BSC nanocomplex reduced the migratory potential of the A-549 cells in vitro. Moreover, the in vivo studies corroborated our in vitro findings and emphasized the decrease in tumor volume of the established xenograft mice model. The histopathological study also confirmed the absence of any noteworthy effects caused by the BSC nanocomplex in the major organs of the treated mice. Thus, the present findings clearly demonstrate that the BSC nanocomplex paves a way as a new agent to be used for therapeutic targeting in cancer treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...