An oral biologics carrier from modified halloysite nanotubes†
Abstract
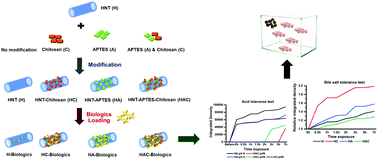
The development of biologic delivery systems for human and animal disease prevention and therapeutics has garnered considerable attention. Although several organic and inorganic materials have been utilized to dispense biological molecules, the carriers of biologics for economic aquatic animals are still limited. Herein, halloysite nanotubes (HNTs), an abundant natural nanoclay, were investigated as a biologic nanocarrier. The surface of the HNTs was modified with aminosilane, chitosan, or both to improve tissue compatibility. The effect of surface modification was also studied to delineate the biologic loading. The biologic releasing patterns of the biologic-HNTs were also observed through the acid-bile salt tolerance test, which mimics the harsh environment of the digestive system, the destination of the biologic-HNTs. The results demonstrated that the bare HNTs and modified HNTs displayed different loading biologic capacities. Similarly, the releasing properties of HNTs were different. Biologics-loaded HNTs were subsequently incorporated in the feed and given to Nile tilapia. A substantial boost of immune response was observed after a couple of weeks in all fish fed with biologics-loaded HNTs. These findings suggest that HNTs are suitable for oral biologic administration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...