Dimethyl trimethylsilyl phosphite as a novel electrolyte additive for high voltage layered lithium cobaltate-based lithium ion batteries
Abstract
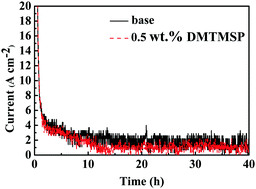
In recent years, in order to meet the increasing demand for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) with high energy density, various positive electrode materials have been developed. The higher the Ni content is, the better the performance of the alloy electrode is and the larger its capacity is. Increasing the charging voltage can improve the capacity of the electrode material and the voltage platform performance. However, as the charging voltage increases, the stability of the interface between the positive electrode material and the electrolyte will decrease, causing an increase in side reactions, which would seriously affect the cycle performance of LIBs. Herein, dimethyl trimethylsilyl phosphite (DMTMSP) was used as an efficient multifunctional electrolyte additive for high-voltage lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2). Protective films would be formed on the positive electrode and the negative electrode surface by electrochemical redox reactions, and the stability of the positive electrode material–electrolyte interface was highly improved whereas the impedance was decreased. On addition of 0.5 wt% of DMTMSP into the electrolyte, the battery exhibited outstanding low-temperature discharge and cycling performances (capacity retention remained at 82.7% at −20 °C with a rate of 0.3C and at 75% at elevated temperature even after 480 cycles).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...