Aging retardation strategy of PVDF membranes: evaluation of free radical scavenging effect of nano-particles
Abstract
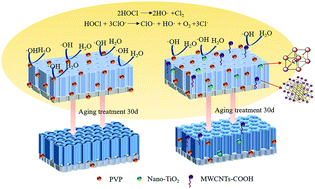
It is very important to reduce the oxidation of free radicals in organic membrane materials for the stability and safety of drinking water production treatment processes. This paper presents a new method for the qualitative and quantitative determination of free radicals in sodium hypochlorite solution by electron spin resonance (ESR) and salicylic acid spectrophotometry. Experiments show that the free radical scavenging rate reaches over 86% after the addition of 0.5 wt% nano-particles. PVDF–PVP/TiO2 and PVDF–PVP/CNT modified membranes are prepared by blending polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) with nano titanium dioxide (nano-TiO2) and carboxyl-modified multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs-COOH), and are treated in 2000 ppm sodium hypochlorite solution for 30 days. Through surface chemistry (FTIR, XRD), surface morphology (SEM), surface hydrophilicity (contact angle), surface electronegative (zeta potential) and mechanical properties tests, the changes of membrane properties are analyzed during aging. The experimental results show that the nano-particles have a quenching effect on free radicals and inhibit defluorination. It has been proved that under the action of nano-additives, the erosion of free radicals on the membrane material is reduced, the aging rate of the membrane material is decreased, and the chemical stability of the membrane material is improved. In this paper, the reason and mechanism of anti-aging of the nano-particle modified membrane are analyzed, which provides theoretical support for future membrane cleaning technology and prolonging the service life of the membrane.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...