Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue under UV and visible light by brookite–rutile bi-crystalline phase of TiO2
Abstract
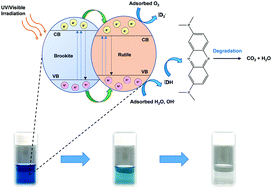
The phase junction of TiO2 nanoparticles plays an essential role in improving photocatalytic activity. Mixed phase brookite–rutile TiO2 nanoparticles with different phase compositions were synthesized through a hydrolysis method using nitric acid of different concentrations. The bi-crystalline phase was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET), UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) and Photoluminescence (PL) analysis. Photoelectrochemical properties were investigated by transient photocurrent density (TPR) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). XRD and Raman results revealed that the brookite content increased in the sample when increasing the HNO3 concentration. The prepared mixed-phase TiO2 nanoparticles have mesopores with large surface areas ranging from 48.81 to 89.95 m2 g−1. UV-vis spectra showed a redshift of absorption edge from 398 nm to 408 nm with increasing brookite content. The optical band gaps which were obtained from the UV-vis spectra were decreased with increasing brookite content. Photoluminescence results showed that the sample prepared with 5.0 M nitric acid (BCTi-4) showed the lowest emission due to the electron–hole recombination. Furthermore, BCTi-4 revealed the highest photocurrent density of 6 μA cm−2 and the smallest Rct values of 3.30 kΩ. The photocatalytic properties of prepared samples were evaluated by the degradation of methylene blue under UV and visible light irradiation. The BCTi-4 exhibited the highest degradation rate that completely degraded methylene blue after 3 hours of UV irradiation and 36 hours under visible light irradiation. This was attributed to the synergetic effect of phase junction of brookite and rutile, which reduces the recombination of photoexcited electron–hole pairs and the optimal ratio of brookite and rutile.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...